Introduction to Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea, located on the Big Island of Hawaii, is renowned as one of the most significant astronomical observation sites in the world. Towering at an elevation of 13,796 feet (4,205 meters) above sea level, it is not only the highest point in Hawaii, but also one of the tallest mountains on Earth when measured from its base on the ocean floor. This impressive height provides a unique geographical advantage, as it places observers above much of the atmosphere, reducing light pollution and atmospheric interference, thereby enhancing astronomical viewing opportunities.
Beyond its physical stature, Mauna Kea holds profound cultural significance for the Native Hawaiian people. It is viewed as a sacred site, embodying spirituality and ancestral connections. The mountain is often referred to as the “White Mountain” due to its snow-capped peak during winter months, which further adds to its intrinsic beauty and allure. Its volcanic origin, features, and diverse ecosystems contribute to a rich tapestry of natural wonder that attracts researchers, tourists, and stargazers from around the world.
The clear, dark skies above Mauna Kea make it an ideal location for observational astronomy, leading to the establishment of several world-class observatories along its summit. These facilities are dedicated to the study of the universe, enabling astronomers to peer into the expanse of the cosmos. As a result, Mauna Kea serves as a gateway for enthusiasts seeking to experience the wonders of stargazing, offering breathtaking vistas of celestial bodies that are often obscured from view in less optimal conditions. The combination of its height, clear atmosphere, and cultural legacy sets Mauna Kea apart as a truly exceptional destination for both scientific exploration and stargazing adventures.
The Significance of Mauna Kea in Hawaiian Culture
Mauna Kea is not just a geological marvel; it holds profound significance within Hawaiian culture and spirituality. This majestic mountain, considered the tallest in the world when measured from its base on the ocean floor, embodies the connection between Native Hawaiians and the heavens. Known as a sacred site, Mauna Kea is revered in various legends and historical narratives that illustrate its central role in Hawaiian tradition.
According to Hawaiian mythology, the mountain is home to deities and ancestral spirits. One prominent figure associated with Mauna Kea is Poliʻahu, the goddess of snow, who is believed to dwell in its peaks. Stories describe how Poliʻahu created snow on the mountain to protect it, emphasizing the sacred relationship between the natural elements and the spiritual world. Additionally, historical accounts recount legends involving the demigod Māui, who journeyed to Mauna Kea to retrieve the sun, further intertwining the mountain with essential Hawaiian narratives that highlight courage and the quest for balance between mankind and nature.
The cultural significance of Mauna Kea extends to contemporary practices, where it is recognized as a place for prayer, reflection, and connection with ancestors. Various traditional ceremonies are performed on its slopes, with practitioners seeking spiritual guidance and renewal. This sanctity is not only a testament to the mountain’s geographical attributes but also to the enduring spirit and resilience of Native Hawaiian identity.
In essence, Mauna Kea embodies a cultural cornerstone for Native Hawaiians, showcasing their rich history, reverence for the environment, and spiritual ties to the cosmos. As such, its preservation and protection are paramount, particularly against threats arising from modern developments that may disregard its cultural values. This underlines the importance of recognizing Mauna Kea not merely as a physical landmark, but as a living entity deeply intertwined with the cultural fabric of the Hawaiian people.
What Makes Mauna Kea Ideal for Stargazing?
Mauna Kea, standing at an impressive height of 13,796 feet, is renowned for being one of the premier destinations for stargazing enthusiasts. Its unique environmental conditions contribute significantly to the clarity and brilliance of the night sky. One of the most crucial factors is its high altitude. At such elevation, Mauna Kea rises above the majority of the Earth’s atmosphere, reducing the atmospheric distortion that typically blurs celestial observations. This altitude allows for a more unobstructed view of the stars, planets, and other astronomical phenomena.
In addition to its height, Mauna Kea is characterized by exceptionally low light pollution. Situated in an isolated area of Hawaii, it is shielded from the bright lights of urban environments, which often hinder the ability to see fainter stars and celestial objects. The combination of minimal artificial lighting and the lack of nearby cities ensures that the skies over Mauna Kea are dark, making it an optimal location for stargazing. This darkness allows for a more vivid display of the universe, enhancing the observer’s experience and enabling the identification of subtle features in the night sky.
Furthermore, Mauna Kea boasts a stable atmosphere, which is vital for clear astronomical observations. The stability of the air above the summit minimizes turbulence, allowing telescopes to achieve higher resolutions. Stargazers often find that conditions for viewing celestial bodies can change rapidly, but at Mauna Kea, the steady atmospheric conditions present a rare opportunity for prolonged and detailed observation. The synergy of Mauna Kea’s high altitude, low light pollution, and stable atmosphere makes it uniquely suited for anyone wishing to explore and appreciate the wonders of the universe as they gaze above the clouds.
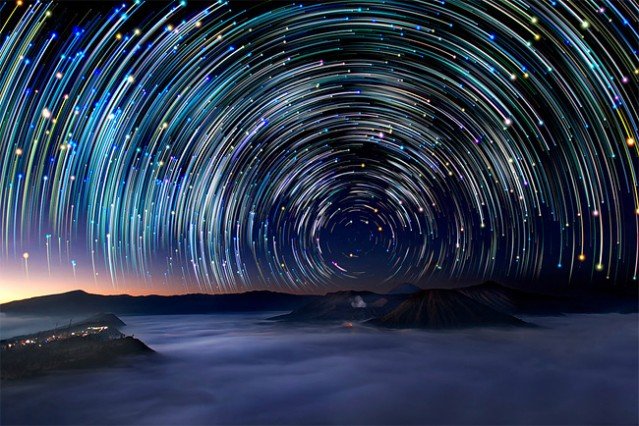
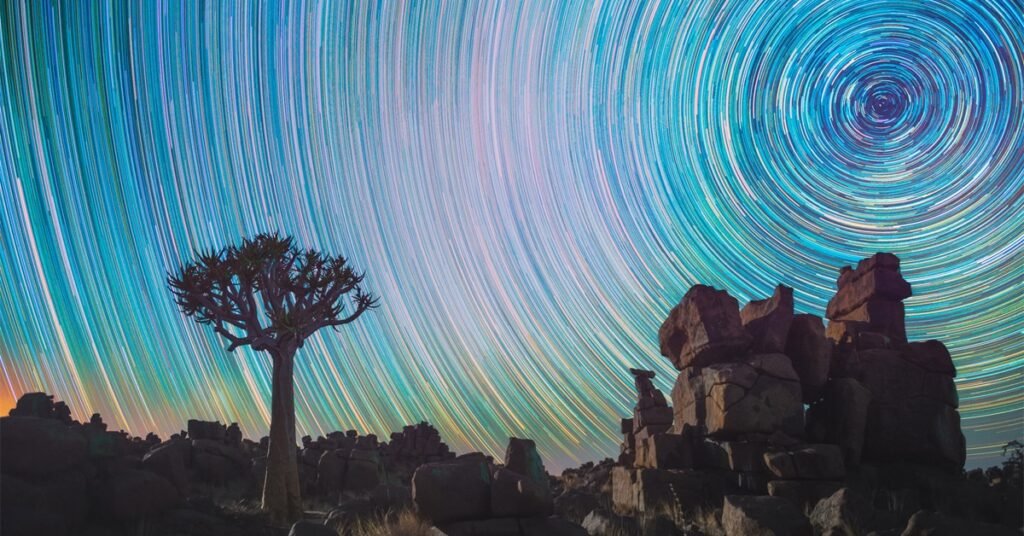
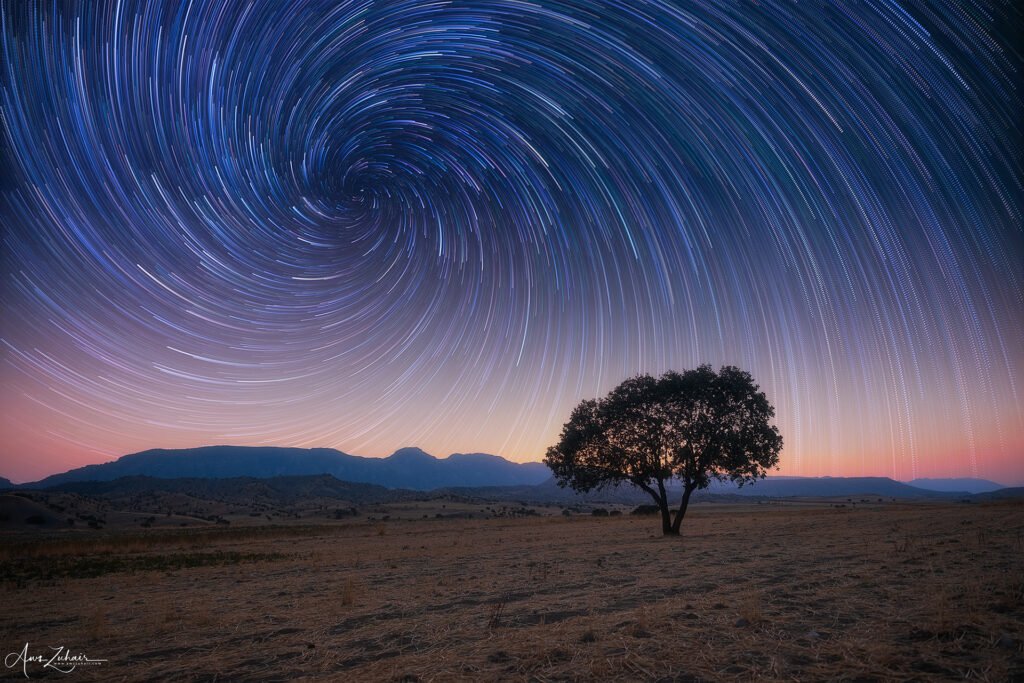



World-Class Observatories on Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea, an alluring volcanic peak situated on the Big Island of Hawaii, is renowned for its exceptional stargazing opportunities. This prominent location hosts several world-class observatories that serve as pivotal research facilities in the field of astronomy. In total, thirteen observatories, including renowned institutions such as the Mauna Kea Observatories and the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, contribute significantly to the advancement of astronomical science.
One of the most notable telescopes at Mauna Kea is the Keck Observatory, which consists of two of the world’s largest optical and infrared telescopes. Each telescope has a primary mirror that measures 10 meters in diameter, enhancing its capacity to gather light and providing astronomers with unparalleled capabilities for celestial observations. The Keck Observatory focuses on various astronomical phenomena, from studying distant galaxies to researching exoplanets, significantly impacting our understanding of the universe.
Another pivotal establishment is the Subaru Telescope, operated by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. With an innovative design and advanced imaging technology, it allows for detailed surveys of the night sky and contributes to various research areas, including galaxy formation and cosmology. Unique among Mauna Kea’s observatories, the Subaru Telescope employs the world’s largest single mirror, thereby maximizing its observational efficiency and capabilities.
The collective efforts of these observatories highlight Mauna Kea’s reputation as a premier astronomical research site. These institutions not only push the boundaries of scientific inquiry but also collaborate on addressing vital questions related to dark matter, star formation, and the origins of the universe. Ultimately, the observatories on Mauna Kea play a critical role in shaping our knowledge of celestial phenomena, solidifying the location’s status as a significant hub for astronomical advancement.
Preparing for Your Visit: What to Expect
As you plan your stargazing adventure at Mauna Kea, preparation is key to ensuring an enjoyable and memorable experience. This majestic destination offers breathtaking views of the night sky, but several factors contribute to making the most of your visit.
Firstly, due to the high altitude of approximately 13,796 feet, visitors should take altitude adjustment seriously. It is advisable to spend time at a lower elevation before ascending to Mauna Kea. Acclimatization helps to reduce the risk of altitude sickness, which can manifest as headaches, nausea, and dizziness. Ensure you stay hydrated and avoid strenuous activities in the days leading up to your visit.
When considering attire, layered clothing is essential. Temperatures can drop significantly at night, even in Hawaii, making it vital to bring warm clothing. A windbreaker, hats, gloves, and comfortable shoes should be included in your packing list. Additionally, bringing a blanket can make your stargazing experience much cozier.
The best time to visit Mauna Kea for stargazing is typically between late autumn and early spring when the skies are clearer and more conducive to celestial observations. Evening visits, especially before twilight, offer optimal viewing conditions. Arriving well before sunset allows you to acclimate and prepare for the stunning show that the cosmos has to offer.
Moreover, packing essentials such as a flashlight (preferably one with a red lens), a camera with a tripod, binoculars or a telescope, and snacks can enhance your experience. A star map or a stargazing app may also prove invaluable in identifying celestial bodies. Preparing accordingly ensures that you maximize your time under the stars while immersing yourself in the grandeur of Mauna Kea.
Stargazing Tours and Experiences
Mauna Kea, renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty and unparalleled skies, offers a variety of stargazing tours and experiences for visitors seeking to explore the cosmos. These tours cater to a range of interests, from novice star gazers to seasoned astronomers. Guided stargazing experiences typically include transportation to the summit, informative sessions led by expert guides, and the availability of high-quality telescopes for enhanced views of celestial wonders.
Top tours in Mauna Kea
The primary advantage of participating in a guided stargazing tour is the wealth of knowledge that expert guides bring to the experience. These professionals are often well-versed in astronomy, geology, and the cultural significance of Mauna Kea, providing insightful commentary that enriches the experience beyond mere observation. For instance, they can explain the intricacies of different constellations, the stories behind them, and the science of celestial events, helping visitors cultivate a more profound appreciation for the night sky.
Additionally, guided tours typically include essential amenities, such as warm clothing, snacks, and hot beverages, which enhance comfort as guests acclimate to the altitude and cooler temperatures of the summit. Many tour operators also provide high-power telescopes, allowing participants to view far-off galaxies, star clusters, and planets in unprecedented detail. Independent stargazing, while rewarding, often lacks these conveniences and insights, potentially leading to a less informative and comfortable experience.
For those less familiar with astronomy or for families with children, guided tours offer a structured approach to stargazing that fosters engagement and learning. The combination of expert guidance, appropriate equipment, and the communal atmosphere of group tours makes the stargazing experience on Mauna Kea not just an event, but a memorable adventure. Overall, while independent stargazing can be enjoyable, the benefits of a guided tour greatly enhance the experience, making it a worthy consideration for anyone visiting this iconic destination.
Safety Considerations at High Altitude
When planning a visit to Mauna Kea for stargazing, it is essential to acknowledge the potential risks associated with high-altitude environments. The summit of Mauna Kea stands at an impressive elevation of 13,796 feet (4,205 meters), which can lead to altitude sickness for some individuals. Symptoms often include headaches, nausea, dizziness, and fatigue, which can compromise the overall experience. Therefore, understanding how to mitigate these risks is essential for a safe visit.
To minimize the possibility of altitude sickness, visitors are encouraged to acclimatize gradually. It is advisable to spend some time at intermediate elevations before heading to the summit; for example, visiting the nearby Mauna Kea Visitor Information Station located at 9,200 feet (2,804 meters) allows the body to adjust to lower oxygen levels. For those who are more susceptible to altitude sickness, ascending slowly and avoiding strenuous activities at higher elevations are crucial. Additionally, recognizing personal limits and descending if symptoms become severe should not be overlooked.
Staying hydrated is another vital aspect of high-altitude safety. The air at higher elevations tends to be much drier, which can lead to dehydration. It is recommended that visitors drink plenty of water to maintain hydration, ideally starting this practice a day before the ascent. Aside from hydration, maintaining adequate nutrition with balanced meals can provide the necessary energy to enjoy the experience fully. Furthermore, it’s wise to dress in layers; temperatures at the summit can drop dramatically, so being adequately prepared with appropriate clothing will enhance comfort.
Lastly, visitors should be informed about the available safety resources, including emergency services and weather updates. Awareness of these factors will contribute significantly to a safe and enjoyable adventure while marveling at the stunning night sky above Mauna Kea.
Photographing the Night Sky
Capturing the majesty of the night sky from Mauna Kea can be an exhilarating experience for photographers of all skill levels. With its high altitude and clear atmospheric conditions, this location offers an unparalleled opportunity to photograph stars, planets, and even the Milky Way. To begin, selecting the right equipment is crucial. A DSLR or a mirrorless camera with manual settings is recommended, as it provides the flexibility needed to adjust for low-light conditions. A sturdy tripod is also essential to ensure stability during long exposures, which can range from 15 to 30 seconds.
When it comes to camera settings, start by selecting a wide aperture, ideally f/2.8 or lower, to allow maximum light to reach the sensor. A higher ISO, such as 1600 to 3200, is advisable, but balance it carefully to avoid excessive noise in your images. Adjust the shutter speed based on the focal length; a good rule of thumb is the 500 rule, which suggests dividing 500 by your lens’s focal length to prevent star trails. For instance, if you are using a 24mm lens, the maximum exposure time should be approximately 20 seconds (500/24).
Finding optimal locations around the observatories is fundamental for successful astrophotography. While the summit of Mauna Kea is popular, consider venturing to nearby locations such as the Onizuka Center for International Astronomy. With fewer obstructions and minimal light pollution, these sites enhance your chances of capturing striking images. Arriving early allows you to scout the area and set up your composition before the stars begin to emerge. Lastly, don’t forget to bring spare batteries and memory cards, as cold temperatures can deplete battery life rapidly, ensuring you’re prepared for a productive night under the heavens.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Experience Like No Other
Stargazing at Mauna Kea represents a truly unique opportunity to immerse oneself in the beauty and grandeur of the cosmos. Elevated at over 13,000 feet, Mauna Kea is not just the highest point in Hawaii but also one of the world’s premier astronomical observatories. Its elevation and remote location offer exceptionally clear skies, allowing for impeccable visibility of celestial bodies that many urban locations simply cannot match.
The experience begins with the journey up the mountain, where visitors are greeted with breathtaking vistas and ever-changing landscapes. As you ascend, the climate transforms, creating a magical atmosphere that prepares you for the eventually revealing of the night sky’s splendor. Once night falls, the sky comes alive with countless stars, planets, and constellations, bringing you face-to-face with the vastness of the universe. Observing these twinkling lights instills a profound sense of awe and wonder, reaffirming our small yet significant place within the cosmos.
Beyond the astronomical wonders, stargazing at Mauna Kea fosters a deeper connection to Hawaiian culture. The mountain is sacred in Hawaiian tradition, and its cultural significance adds layers to the stargazing experience. Visitors often find themselves reflecting on the rich history and mythology associated with the stars and the universe. This blend of natural beauty and cultural heritage creates a holistic experience that transcends mere observation; it invites exploration and contemplation of humanity’s relationship with the universe.
In essence, the cosmic experience at Mauna Kea is not just about witnessing the night sky; it is an invitation to marvel at the wonders that lie above. This journey leaves an indelible mark on the hearts of all who partake, making it an unparalleled adventure into the depths of the universe.